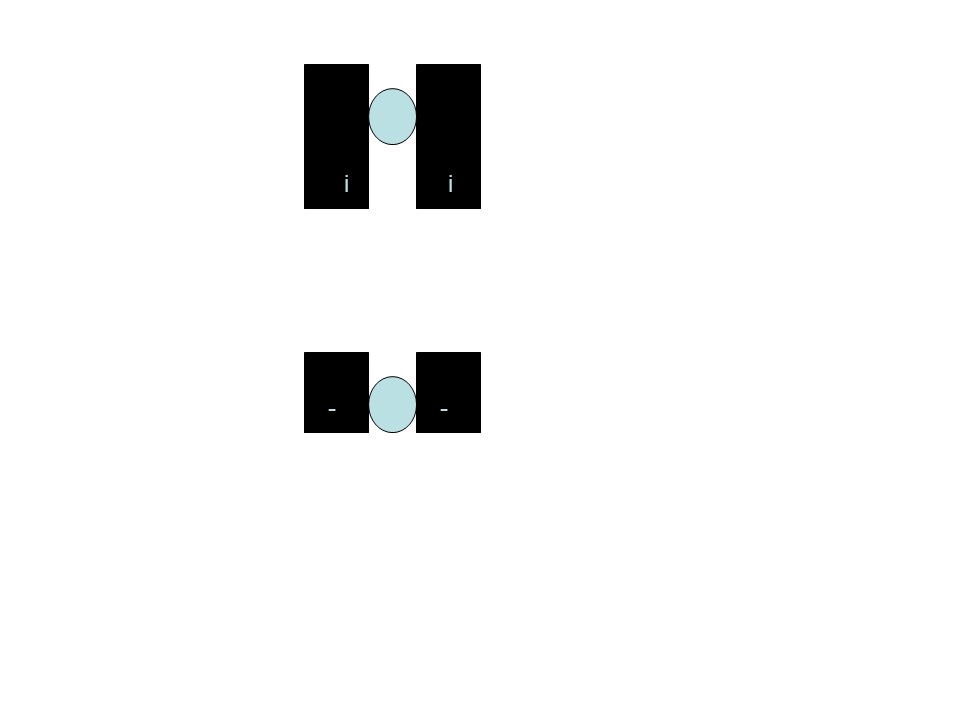Meiosis is a tricky concept. To help to you understand it, go through the following activities in order
Start by watching this video
[youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=toWK0fIyFlY&w=560&h=315]
While you are watching this video, do the following worksheet:video_recap_of_meiosis_by_amoeba_sisters_final
(You may want to print this out)
Here are the objectives for this unit. lets take them one at a time
1. Be able to determine whether a cell is in Mitosis, Meiosis 1 or Meiosis 2
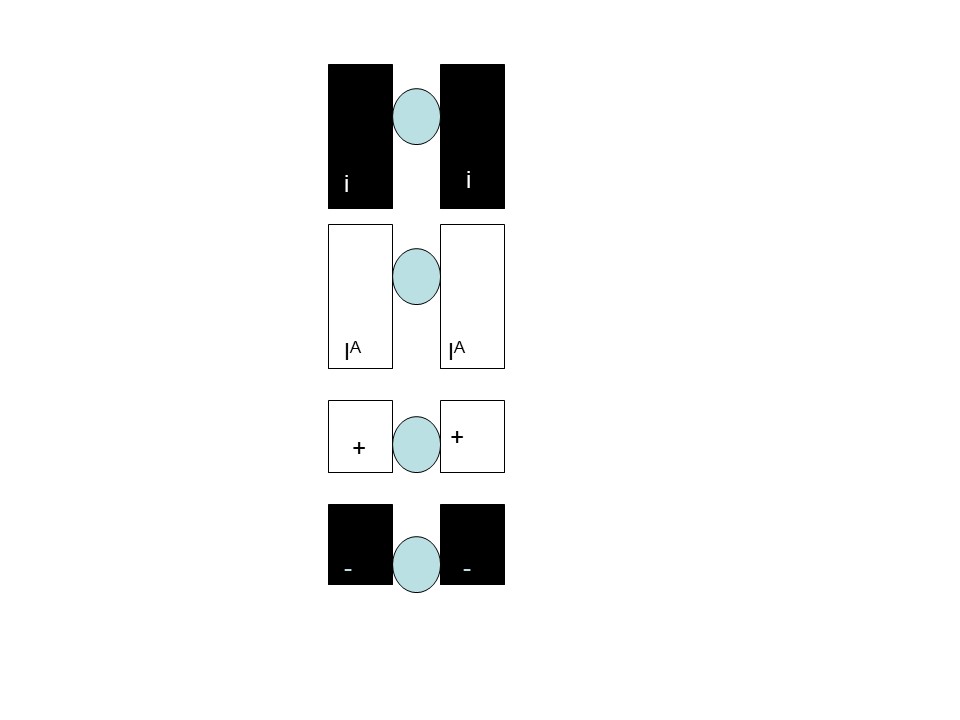
To be able to do this, one first needs to be able to distinguish sisters and homologues as shown in this slide
The Sisters are genetically identical (before recombination, which we will ignore for the moment)
The homologues contain the same genes but can contain different genetic information (for example A versus B blood type)
In M1, the homologues consist of 2 sisters which remain attached to each other. The homologues separate from each other in M1. Thus all M1 cells will show a row of 4 sisters as shown in the bottom of the figure. You will not see this in any other stage. Thus it is easy to distinguish M1 from other stages.
In M2, the sisters separate. The homologues have already separated. Thus one should never see both homolgoues in an M2 cell
Now how do we distinguish M1 from mitosis
(1) Mitotic cells contain all chromosomes that an individual has. Therefore
(A) For each chromosome they should show one homologue from their mother and one from their father. Meiotic cells show only the maternal or paternal chromosome, not both
(B) Because of (A) mitotic cells will always have an even number of chromosomes. Cells in M2 can have an odd number of chromosomes. During anaphase, a mitotic cell will have an even number of chromosomes on each side of the metaphase plate, an M2 cells can have an odd number on each side of the plate. (this is true for an organism such as humans for which the total number of chromosomes is an odd number X 2. (46 for humans).
(C) Recombination does not occur in mitosis. If you see a recombinant chromosome (partly one color and partly another), it must not be in mitosis.
(D) If X and Y chromosomes are present (This will be indicated) A mitotic cell can have both the X and the Y (if it is male) but a cell in M2 can only have the X or the Y.
Now lets try some examples. What stages are the following cells?. The black chromosomes come from the father and the white from the mother. Ignore the symbols, they are too small to read and are not needed for this exercise.
The middle one is?
The bottom one is?
The top one is Meiosis 2. There are no maternal chromosomes at all. Therefore it can not be Mitosis. If it were M1, you would also see equal numbers of paternal and maternal chromosomes and you would see 4 sisters across.
The middle one is Meiosis 1. There are equal numbers of maternal and paternal chromosomes and there are 4 sisters across.
The bottom one is Mitosis. There are equal numbers of maternal and paternal chromosomes and there are not 4 sisters across,
To do more practice problems Copy this code
TTQUVGSI1M
and then go to Socrative.com
When you go to the site, use the student login (this does not require any registration and put the code number where it says “enter Teacher’s room code”
It will ask for a name. You do not need to give your real name. When you are done with the exercise, it will say “teacher waiting or something similar. There will be no more activities at this site.
Be able to compare mitosis and meiosis in terms of processes and end results
The purpose of mitosis is to create cells that are genetically identical to the parent cells. Mitosis gives you cells that have 2 copies of each chromosome, just like the parent cells
The purpose of meiosis is to create cells that have 1 (not 2) copies of each chromosome so that after fertilization, the embryo will have 2 copies of each chromosome.
In both process, there is a preceding interphase which includes chromosome duplication.
Both processes have prophase, metaphase Anaphase and Telophase using the same cellular structures such as spindles and centrioles. Meiosis has 2 sets of these stages.
In order to assure that egg and sperm only get one of each chromosome, the homologues (members of a pair) line up during M1 and separate. During M1, crossing over occurs between homologues, this results in increased genetic variation
Crossing over does not occur in mitosis.
By Anchor207 (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Be able to distinguish homologues and sisters and know when in meiosis they separate
As said before Homologues have the same genes but may have different versions (Alleles) Homologues separate at M1. Sisters are initially (before recombination) genetically identical. They separate at M2. (They also separate during mitosis)
Be able to order the steps of meiosis
Chromosome Duplication (Before meiosis) Then Pairing of Chromosomes (Prophase of M1) Crossing Over (Prophase of M1) separation of Homologues (Anaphase of M1) separation of sisters (Anaphase of M2)
Think you know it? Try this? (click on the buttons in the correct order)
//scratch.mit.edu/projects/embed/48881454/?autostart=false
Know how meiosis leads to genetic variation (Know how recombination and independent assortment can increase the variation in gametes)
Recombination can lead to different combinations of alleles (gene variants) on the same chromosome
Independent assortment See page 263. Figure 13.11. See that there are 4 possible combinations of chromosomes when there are 2 pairs. As a rule, the number of possible combinations is 2^N (2 to the Nth) power where N is the number of pairs of chromosomes. Thus a male can have 2^23 possible combinations or over 8 million possible sperm. And that is without recombination!
Final exercise.
//scratch.mit.edu/projects/embed/11743273/?autostart=false
Use the attached worksheet
Meiosis Activity